
Almost every site now loads over HTTPS, encrypting web traffic in the process. It’s the new normal for web security. But here’s the kicker – while encryption keeps your data safe, it’s like a sealed letter. What if someone’s slipping nasty stuff in there?
Enter SSL Inspection, the SSL security guard. Think of it as the organization’s own detective, checking out the encrypted traffic and SSL certificates, ensuring there’s no malicious mischief going on.
So, what is SSL inspection? It’s the method that peeks inside encrypted messages, not to invade privacy but to keep the digital landscape safe and sound.
In this read, we’ll discuss SSL inspection without drowning in tech talk. It’s a security measure organizations take to see what attackers might be cooking up to find those sneaky vulnerabilities.
Stay with us as we break it down, showing its strengths and weaknesses.
Table of Contents
- What is SSL Inspection?
- How Does SSL Inspection Work?
- SSL Inspection Benefits and Disadvantages
- How to Bypass Malicious SSL Inspection?
What Is SSL Inspection?
SSL inspection is a security process that monitors encrypted network traffic. It is also known as SSL interception, TLS inspection, HTTPS interception, or HTTPS inspection.
SSL inspection analyzes encrypted data transmitted over a network using the SSL/TLS protocol. This inspection allows organizations to study the content of encrypted HTTPS traffic to ensure security and compliance.
In essence, SSL inspection involves ‘eavesdropping’ on secure connections. And, while it may seem like an espionage tactic, it’s a security measure to keep a network safe.
The SSL/TLS protocol secures communication between a user’s web browser and a website, ensuring that the data exchanged remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access. However, attackers can also employ it to hide threats, such as malware or other security risks, within the encrypted SSL traffic.
Enterprises, educational institutions, government agencies, and Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) all utilize SSL inspection to detect potential threats, ensure policy compliance, and protect sensitive information.
How Does SSL Inspection Work?
It all begins when you make an SSL-encrypted request to a website. Usually, your browser would directly communicate with the website’s server to establish a secure connection. However, if an SSL inspection tool is in place, it acts as an intermediary between your browser and the server.
The SSL inspection interception device, often referred to as a middlebox, first intercepts your request, establishing an SSL connection with your browser as if it were the server. It then makes its own secure connection to the server on your behalf.
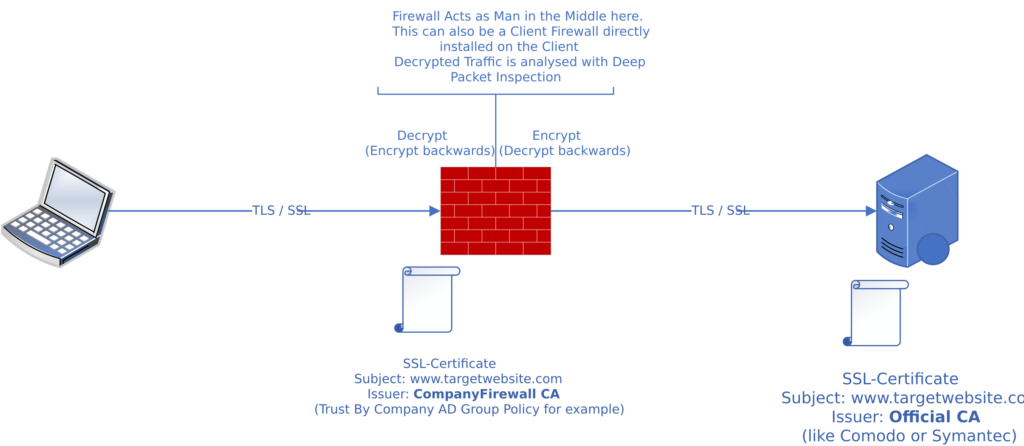
This way, it decrypts, inspects, and re-encrypts the data flowing between you and the server. If it detects any malicious activity, it can block it before it reaches your device.
However, it’s not all about defense. SSL traffic inspection also ensures that the re-encrypted data sent to you corresponds with your organization’s security policies. For example, it can prevent sensitive information transmission outside the network.
SSL Inspection Process Step-By-Step
Here’s the complete SSL inspection HTTPS breakdown, step-by-step:
- Client Initiates Secure Connection: The user accesses a secure site.
- SSL/TLS Handshake and Certificate Verification: The server sends its certificate and the client checks authenticity.
- SSL Inspection Trigger and Certificate Replacement: Middlebox intercepts and replaces it with a new certificate.
- Encrypted Tunnel with Middlebox and Data Decryption: The client connects to the middlebox; it decrypts content.
- Content Inspection and Re-Encryption for Client: Deep inspection for threats; if safe, re-encrypts for the client.
- Secure Connection to Server & Data Exchange: Middlebox connects securely to the server, forwarding requests, receiving responses, and re-encrypting for the client.
SSL Inspection Benefits and Disadvantages
Now, let’s weigh the pros and cons of SSL inspection. You’ll see how it can enhance network security, but also why there are some privacy concerns.
SSL Inspection Benefits
By revealing hidden threats in encrypted traffic, SSL inspection detects malware, phishing scams, and other cyber threats that might otherwise go unnoticed.
It also allows for detailed data loss prevention, as it gives you control over what information leaves your network. Moreover, SSL inspection provides compliance with regulations that require inspection of encrypted HTTPS traffic.
- Enhanced Security: SSL inspection allows for the deep inspection of encrypted traffic flowing to the client, uncovering potential threats and vulnerabilities within secure connections, including phishing attacks, Zero-Day exploits, and advanced persistent threats (ATP).
- Malware Detection: HTTPS inspection identifies and prevents malware injection and other malicious content that attackers may conceal within encrypted communication channels.
- Data Loss Prevention: SSL inspection prevents unauthorized data exfiltration by analyzing the content of encrypted traffic, ensuring sensitive information doesn’t leak through secure connections.
- Policy Enforcement: Organizations can enforce acceptable use policies and regulatory compliance by inspecting SSL-encrypted traffic, monitoring for policy violations, and taking appropriate actions to mitigate risks.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: TLS inspection allows organizations to integrate threat intelligence feeds, which are real-time databases of known malicious attacks and entities, helping them stay informed about emerging cyber threats within secure communication.
SSL Inspection Disadvantages
Decrypting, inspecting, and re-encrypting SSL traffic can slow down network performance. Sure, it may not be a significant issue for smaller networks, but for larger organizations with heavy data traffic, it could cause problems.
Also, SSL inspection can introduce security risks. If not properly managed, it can create vulnerabilities that cybercriminals could exploit. Here are a few of them:
- Certificate Trust Issues: SSL inspection relies on a certificate on the inspection device. If users don’t trust this certificate, it can lead to security warnings or errors, potentially exploited by attackers for man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Key Management Challenges: Poorly managed private keys used in SSL inspection pose a risk. If compromised, attackers could decrypt sensitive information.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Decrypting and inspecting secure communication raises privacy concerns; organizations must handle decrypted data responsibly to comply with regulations and protect user privacy.
- Increased Attack Surface: SSL packet inspection adds an extra attack surface. and attackers may target middlebox vulnerabilities. When the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s US-CERT issues an alert warning about exposures in HTTPS inspection products, you know it requires careful consideration.
- Resource Exhaustion: SSL traffic inspection can be resource-intensive. Attackers may overwhelm the inspection device, causing resource exhaustion and potential service disruption, highlighting the need for rate limiting and resource monitoring.
How to Bypass Malicious SSL Inspection?
You’ll need to use a few tools to bypass malicious SSL inspection as it can pose serious privacy and security threats when used with ill intent. Your data might unintentionally fall into the wrong hands, and your online activities could be tracked without your consent.
- Firstly, you can use a VPN (Virtual Private Network). A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it difficult for anyone to inspect your data. It creates a secure tunnel between your device and the internet, effectively helping you bypass SSL inspection.
- Another approach is to use the Tor browser. Tor works by bouncing your traffic through several servers worldwide, making it hard for anyone to track your online activities. It’s an effective tool to shield your data from malicious SSL inspection.
- You can also consider using HTTPS Everywhere, a browser extension that encrypts your communications with many major websites. It ensures you always connect to the secure (HTTPS) version, even if the site doesn’t offer such a version. It can help you bypass SSL inspection by protecting your data from being intercepted.
- Lastly, always stay updated with the latest security patches and updates. Cyber threats evolve rapidly, and older SSL inspection software or encryption algorithms may not offer adequate protection.
Bottom Line
Hopefully, this article answered the “What is SSL inspection?” question for you. You’ve learned that SSL/TLS inspection is a security measure that decrypts and checks SSL-encrypted traffic for threats. It works by acting as an intermediary between the client and the server.
As with any other security tool, it has both benefits and drawbacks. It’s a fine line to tread between security and privacy, but understanding SSL inspection helps you make informed decisions when assessing your organization’s exposure to cyber threats.
Save 10% on SSL Certificates when ordering today!
Fast issuance, strong encryption, 99.99% browser trust, dedicated support, and 25-day money-back guarantee. Coupon code: SAVE10



























